Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Polish forests
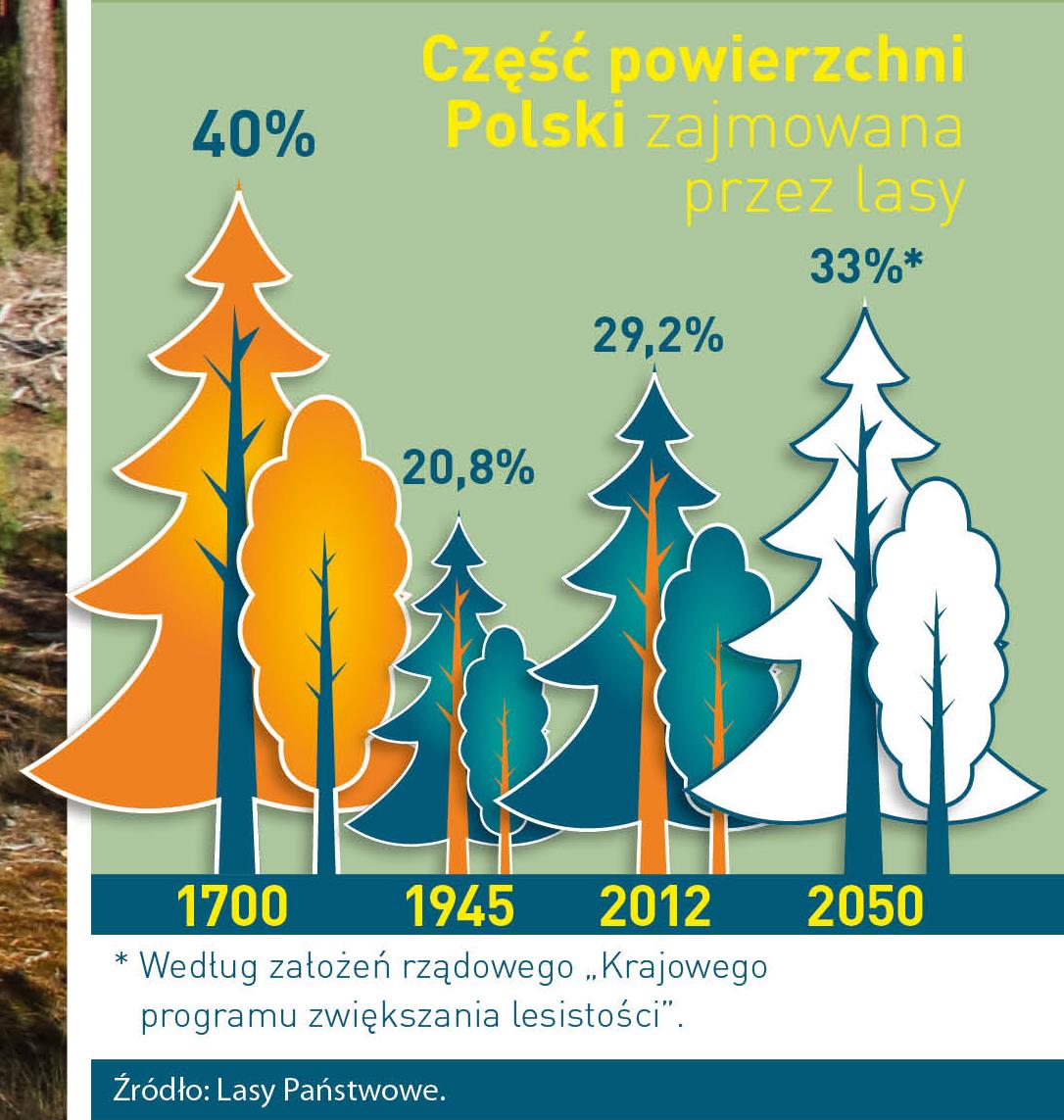
Poland is in the European lead, while concerning the area of all forests. They cover about 29,2 % of the country territory, and grow within the area of 9,1 million hectares. The overwhelming majority of the forests is state owned, of which almost 7,6 million hectares are managed by the State Forests National Forest Holding..
The number of Polish forest is still growing. The forestation rate of the country has increased from 21 % in 1945 to 29,2 % at the moment. Between 1995 and 2008, the forest area increased by 310 thousand ha. The basis for afforestation works is the "National Programme for Increasing the Forest Cover" (KPZL), assuming an increase of the forestation rate up to 30 % by 2020 and up to 33 % by 2050. Polish forests abound in flora, fauna and fungi. 65 % of the total number of animal species live there.
The forests grow in our country on poor soils, mainly because of the development of the agriculture in previous years. It influences the distribution of the types of the forest sites in Poland. Over 55 % of the forest areas is covered with coniferous forests. In other areas, there are forest sites, mainly the mixed ones. Their small part constitute alder and riparian forests – not more than 3 %.
In the years 1945 – 2011 the area of natural deciduous tree stands within the area of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %.
Within the lowlands and uplands the most often occurring tee species is pine. It covers 64,3 % of the forest area of the State Forests National Forest Holding and 57,7 % of private and commune forests. In the mountains the predominant species is European spruce ( in the west) and European spruce with beech (in the east). Domination of pine is the result of carrying on sustainable forest management in the past. Once, the monocultures (crops or cultivations of one species) were the answer to the great demand of industry for wood. Such forests appeared to be quite fragile to climatic factors. They also were often the prey of pests' expansion.
In Polish forests, the share of other tree species, especially deciduous trees have been systematically increasing. The foresters have stepped aside from monocultures – that is why, they try to fit specific species of the forest stand to the natural stand, that would be proper for the given area. Thanks to that, in the years 1945 – 2011, the area of the deciduous tree stands within the lands of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %. There occur more and more frequently the following tree species: oaks, ashes, maples, sycamore maples, elms, but also birches, beeches, alders, poplars, hornbeams, aspens, tilias and willows.
Our forests are the most often represented by the forest stands aged 40 to 80 years. The average age of the forest equals 60 years. More and more trees are of big size at the age over 80 years. Since the end of the Second World War, the forests' area has increased up to almost 1,85 million hectares.
Raport o stanie lasów w Polsce 2012
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Lasy Nadleśnictwa
Lasy Nadleśnictwa
 Las jesienią fot. L. Kopińska
Las jesienią fot. L. Kopińska
 Lasy Nadleśnictwa są zróżnicowane siedliskowo fot. L. Kopińska
Lasy Nadleśnictwa są zróżnicowane siedliskowo fot. L. Kopińska
 Śródleśne łąki fot. L. Kopińska
Śródleśne łąki fot. L. Kopińska
 fot. L. Kopińska
fot. L. Kopińska
 Leśne bagienka fot. L. Kopińska
Leśne bagienka fot. L. Kopińska
 fot. L. Kopińska
fot. L. Kopińska
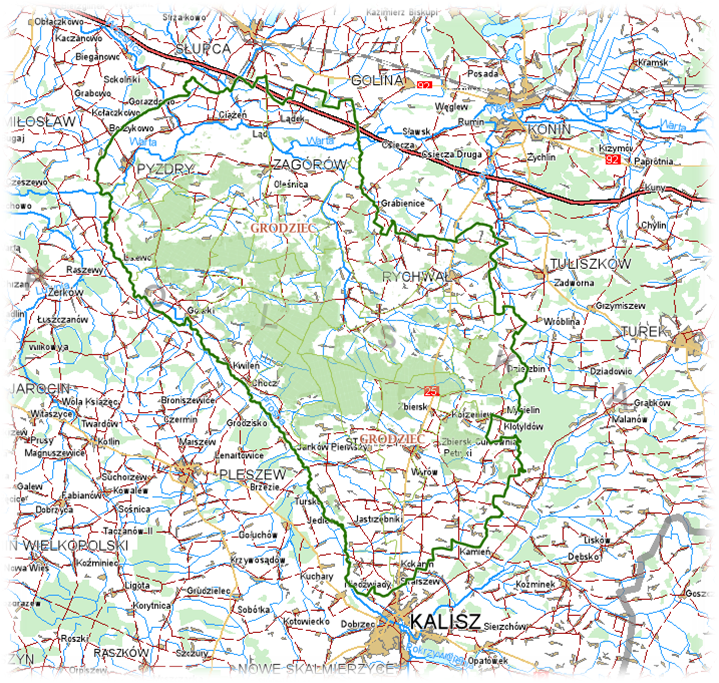
Nadleśnictwo Grodziec gospodaruje na terenie o pow. 25 tys. hektarów.Teren jest zróżnicowany.Zapraszamy do korzystania z walorów lasu
Nadleśnictwo Grodziec w całości położone jest w zasięgu województwa wielkopolskiego na terenie 5 powiatów: Konin, Kalisz, Pleszew, Słupca i Września.
Powiat koniński - gminy: Grodziec, Rychwał, Rzgów
Powiat kaliski - gminy: Blizanów, Ceków Kolonia ,Mycielin, Stawiszyn, Żelazków
Powiat pleszewski - gminy: Chocz, Gizałki
Powiat słupecki: - gminy: Lądek i Zagórów
Powiat wrzesiński - gmina Pyzdry.
W aktualnej strukturze organizacyjnej Nadleśnictwo Grodziec gospodaruje na powierzchni 25513 ha, w tym 24955 ha powierzchni leśnej.
Obecny zasięg terytorialny Nadleśnictwa wynosi 1225 km2.
Średnia powierzchnia leśnictwa wynosi 1595 ha.
Mapa Nadleśnictwa Grodziec
Cały obszar leży w dorzeczu Warty, odwadniają go lewobrzeżne dopływy tej rzeki Prosna i Czarna Struga.
Nadleśnictwo Grodziec jest położone pomiędzy dwoma dużymi ośrodkami miejskimi; Kalisz i Konin. Około 30% obszaru leży na terenie powiatu kaliskiego
Dominuje w tym regionie gospodarka rolno- leśna. Dominują drobne gospodarstwa rolne i leśne. Kilka gospodarstw zmieniło swój profil na agroturystyczny. Zauważalny jest wzrost liczny osób, które rozwinęły własną działalność gospodarczą.
Sieć dróg powiatowych i gminnych jest dobrze rozwinięta, natomiast brak jest czynnych linii kolejowych.
Obszar Nadleśnictwa położony jest na obszarze nizinnym. Dominuje teren równy. Piaski rzeczno-lodowcowe oraz jeziorne złożone są na rozległych równinach. Wraz z piaskami wydmowymi są przyczyną występowania na terenie siedlisk ubogich.
Jesień w lesie fot. L. Kopińska
Występują tutaj pola wydmowe oraz pojedyncze wydmy. Są to tzw. "stare wydmy" utworzone po ustapieniu lodowca z terenu Wielkopolski. Wydmy na terenie Nadleśnictwa układają się w większości w ciągi na kierunku wschód-zachód. Niektóre z nich dochodzą do 6 km długości. Wysokość wydm kształtują się w rozpiętości od 3 m do 30 m.
Znaczny obszar Nadleśnictwa jest lekko sfalowany.
Teren charakteryzuje się dużą mozaikowatością występowania utworów glebowych. Ma to silny związek z ukształtowaniem terenu oraz występowaniem wód gruntowych w zasięgu profilu.
Pod względem hydrograficznym cały obszar Nadleśnictwa położony jest w dorzeczu rzeki Warty. Wody spływu powierzchniowego odprowadzone są do Warty przez jej lewobrzeżne dopływy: Prosnę i Czarną Strugę oraz ich dopływy. W obszarze terytorialnego zasięgu Nadleśnictwa brak jest jezior. W związku z niskimi sumami opadów duże znaczenie dla rozwoju drzewostanów mają głębokość i zasobność wód gruntowych.


 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański